- Home
- Crop Knowledge
- Fruits
- Sapota
Sapota
- Nutrients
- Common Pests
- Crop Selection
- Documents
|
Crop Stage Images |
 |
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of the tree | 1 Year Old | Annual Increase (2-5 Years) |
6th Year Onwards | |
|
Nutrients (Kg/tree) |
FYM |
10 |
10 | 50 |
| N | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1 | |
| P | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1 | |
| K | 0.30 | 0.30 | 1.5 | |
Deficiency of Nutrients:
| Nutrients | Nitrogen (N) | Phosphorus (P) | Potassium (K) | Calcium (Ca) | Magnesium (Mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients Deficiency |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Deficiency Symptoms | 1. Stunted growth.
2. The bark of the shoots turned reddish-brown in colour. 3. On elongating shoots the immature leaves were amber to bright red in colour while the mature leaves remained small and yellow-green in colour. 4. Early abscission of leaves, smaller and fewer fruits. |
1. Pigmentation seen in older leaves; leaf size becomes small. | 1. Light brown specks scattered all over the leaves which appeared later merged forming necrotic patches between the large veins.
2. Browning on the underside of the leaves and chlorotic areas between veins due to K deficiency. |
1. Tip of the twig and flower bud affected. | 1. Leaves become lighter green which gradually turned greenish yellow, remaining deeper green along the midrib and larger veins.
2. Leaves turned yellow with a scattered brown lesion on the leaf blade. 3. Interveinal chlorosis on older leaves followed by necrosis of distal leaf edge. |
| Nutrients | Sulphur (S) | Boron (B) | Copper (Cu) | Iron (Fe) | Manganese (Mn) | Zinc (Zn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients Deficiency |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Deficiency Symptoms | 1. Yellowing of young leaves; growth of the leaf will be affected. | 1. Leaves were yellowish-green in colour the older leaves showed signs of burning at the tips and along the margins which abscissed prematurely.
2. The tip burning of young leaves and splits or crack on the midrib and large veins on the underside of the leaf. |
1. The leaf veins developed a reddish-brown colour, premature defoliation and dieback of twigs also occurred.
2. The tip of the twigs developed multiple buds which died soon. |
1. Yellowing of young leaves; Occurrence of interveinal chlorosis. | 1. Light coloured spots on the leaves and sometimes necrotic spots also appear.
2. Green bands of varying width appear along the midrib and veins with yellow areas between the veins. 3. Interveinal chlorosis, premature dropping of the leaves and dye back of terminals due to Mn deficiency were also recorded. |
1. Symptoms seen in young leaves; The size of the leaf become small. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Freshly laid eggs were soft, pale yellow but semi-transparent and fertile eggs turned pink. | Neonate larvae it is pink and become yellow within 24 h and later turns into greenish in colour. Head is pale yellow. | Pupation takes place in plant debris or in the soil. | The adult is greyish in colour with compound black eyes with setaceous antennae.
Fore wings are grayish with four black transverse wavy lines |
| Life Cycle: | 4-10 Days. | 2-12 Days. | 8-10 Days. | 75-80 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray with 0.1 % carbaryl. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | A female moth lays eggs on medium sized immature fruits of sapota. | The larvae are very minute, white in colour with a pinkish tinge. | Make a fine shell-like structure within which it pupates. | The adult is a small delicate greyish white moth with bell-shaped wings and resembles bird droppings. |
| Life Cycle: | 7-10 Days. | 6-7 Days. | 9-11 Days. | 20-25 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spraying of profenophos 0.04% or Lambdacylothrin 0.025% or deltamethrin 10 ml/10 lits of water. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | The eggs were smooth, oval and white in colour at the time of oviposition and turned to light brown before hatching . | The larva is small, slender, pinkish brown with black head and passed through four instars on sapota buds.
The newly hatched caterpillar was light yellow in colour. |
This pre-pupal condition lasted for about one day during which the larva did not exhibit any movement unless it was disturbed. | Grey moth with a black patch on wings.
The adult’s development was completed and legs and the wings are clearly visible through the pupal skin under a microscope. |
| Life Cycle: | 4-6 Days. | 4-5 Days. | 2-3 Days. | 20-25 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray phosalone 35 EC 2 ml/lit or phosphamidon 40 SL 2 ml/lit. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: | 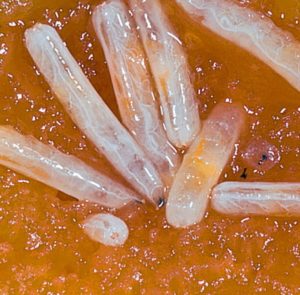 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae(Maggot) | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Female flies insert eggs under the skin of fruit in clusters. | The white maggot is legless and resembles an elongated cone. The mouth is at the pointed end of the body. | When mature, maggot drops to the ground and pupates in the soil.
The puparium is yellowish-brown and seed-like. |
Generally, the abdomen has two horizontal black These markings may form a “T” shaped pattern |
| Life Cycle: | 5-8 Days. | 11-15 Days. | 9-10 Days. | 10-15 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Use bait spray combining any one of the insecticides and molasses or jaggery 10 g/l, fenthion 100EC 1ml/l, malathion 50EC 2 ml/l, dimethoate 30 EC 1 ml/l, carbaryl 50 WP 4 g/l.
Prepare bait with methyl eugenol 1% solution mixed with malathion 0.1%. Spray fenthion 100 EC 2 ml/ lit or malathion 50 EC 2ml/lit. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | The eggs are brownish-white, cylindrical | Yellowish-white, with the head dark brown and sclerotized, without obvious legs. | Reddish setae on labrum and bases of mandibles and antennae. | Covered with grey to yellowish pubescence on a dark brown to a pitchy surface. |
| Life Cycle: | 1-2 Weeks. | 10-45 Days. | 19-36 Days. | 6 Months. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Swab Coal tar + Kerosene @ 1:2 or Carbaryl 50 WP 20 g / l on the basal portion of the trunk ( 3 feet height).
Padding with dimethoate 10 ml in 2.5 cm /tree soaked in absorbent cotton. Apply carbofuran 3G 5 g per hole and plug with mud. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Forewings are reddish brown spot ringed with white. | Yellowish brown with black spots and long lateral tufts of hairs. | Hind wings are white. | Greyish head and thorax and whitish abdomen. |
| Life Cycle: | 7-10 Days. | 10-20 Days. | 7-10 Days | 30-40 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray chlorpyriphos 20EC or phosalone 2 ml/l.
Spraying of cypermethrin 0.025%. Dusting carbaryl 10 D on the trunk and branches (around the tree 4 feet). |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Nymphs | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Female laid eggs in groups which lay beneath the body . | Pure white in colour. | Soft-bodied, flat and waxy, mealybugs can also be identified by their oval shape and body segmentation. |
| Life Cycle: | 20-29 Days. | 26-57 Days. | 36-53 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray methyl demeton 25 EC@ 0.05%or dimethoate 30 EC @ 0.06%. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Microfeed L 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Eggs are whitish green and elongate-oval and are laid singly and hatch beneath the female where they are protected. | Nymphs or immature green scales are oval, flat and yellowish green in colour, and have six short legs. | The adult female is shiny pale green with a conspicuous black, irregular U-shaped internal marking that is dorsally visible to the naked eye. |
| Life Cycle: | 4-12 Days. | 10-12 Days. | 20-25 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray chlorpyriphos 2ml/lit or phenthoate 1ml/lit.
After two weeks release 20 predator beetles viz., Cryptolaemus montrouzieri beetle per tree. Encourage parasitoids viz., Aneristis sp Coccophgagus cowperi, C. bogoriensis |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Seed Variety | Characteristics | Crop Yield (fruits/tree) |
|---|---|---|
| Kalipatti | 1. Popular table purpose of variety, Leaves broad, thick and green in colour. 2. Fruits oblong/round, borne in single, fruit quality high with soft sweet pulp, main picking season winter. |
350-400 |
| Co.1 | 1. Bearing after 4 years of planting. 2. Fruits large, oblong, sweet, flesh reddish brown, weight 125 g, TSS 18%. |
175 to 200 kg |
| Co.2 | 1. Tree medium in height, fruit oblong-round, medium-sized, flesh soft juicy, sweet, gritty, light brown in colour with a pleasant aroma. TSS 23%. 2. Average wt. of fruit 125-150g |
175 kg |
| PKM 1 | 1. The tree is dwarf and adaptable to Southern and Central districts. 2. Fruits are of two shapes viz., round (rarely) and oval (maximum). The skin is very thin and the pulp has a buttery consistency. TSS 23%. 3. Average fruit wt. 80g. |
3547 |
| CO.3 | Trees are of intermediate stature. Bearing commences from the fourth year of planting. Fruits are dull brown, oblong, sweet. |
157 kg |
| PKM 4 | 1. It is a high yielder with compact canopy and cluster bearing character. 2. It bears spindle-shaped fruits suitable for dry flakes production. 3. It is suitable for varied soil types of tropical conditions. |
100.4 kg |
| PKM 3 | 1. The fruits bear in clusters with oval-shaped large fruits. 2. The vertical growth habit of the tree allows for high-density planting. 3. The variety is tolerant to leaf spot and leaf Webber. |
14 t/ha |

