- Home
- Crop Knowledge
- Vegetables
- Potato
Potato
- Nutrients
- Common Pests
- Crop Selection
- Documents
|
Crop Stage Images |
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Crop Duration | After Sowing | 40 Days After Sowing | |
|
Nutrients (Kg/ha) |
N | 7 | 18 |
| P | 6 | 4 | |
| K | 11 | 26 | |
| Mg | 5 | 4 | |
| S | 5 | 2 | |
Deficiency of Nutrients:
| Nutrients | Nitrogen (N) | Phosphorus (P) | Potassium (K) | Calcium (Ca) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients Deficiency |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Deficiency Symptoms | 1. The yellowing in nitrogen deficiency is uniform over the entire leaf including the veins.
2. Younger leaves turn darker green, older leaves remain yellow. 3. Upward cupping of deficient when severs. |
1. The symptoms first develop on older leaves showing some necrotic spots and plants are dwarfed or stunted.
2. Plants develop a distinct purpling of the stem, petiole and the undersides of the leaves. 3. Lower leaf surface grey-green. 4. Leaflets roll upward, severely if a deficiency is severe. |
1. Since potassium is very mobile within the plant, symptoms only develop on young and full-sized leaves in the case of extreme deficiency.
2. As the deficiency progresses, most of the interveinal area becomes necrotic, the veins remain green and the leaves tend to curl and crinkle. 3. Leaves take on a scorched appearance with black pigmentation and necrotic (dead tissue) edges. |
1. The calcium-deficient leaves show necrosis around the base of the leaves.
2. The very low mobility of calcium is a major factor determining the expression of calcium deficiency symptoms in plants. 3. This ultimately results in the margins of the leaves grow more slowly than the rest of the leaf, causing the leaf to cup downward. |
| Nutrients | Sulphur (S) | Magnesium (Mg) | Iron (Fe) | Boron (B) | Manganese (Mn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients Deficiency |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Deficiency Symptoms | 1. These leaves show general overall chlorosis.
2. The yellowing is much more uniform over the entire plant including young leaves. 3. The reddish colour often found on the underside of the leaves. 4. Leaflet yellowing is uniform and general. |
1. The Mg-deficient leaves show advanced interveinal chlorosis.
2. The symptoms generally start with mottled chlorotic areas developing in the interveinal tissue. 3. Symptoms appear first on young mature leaves. |
1. Iron has low mobility, iron deficiency symptoms appear first on the youngest leaves.
2. Iron deficiency is strongly associated with calcareous soils, anaerobic conditions, and it is often induced by an excess of heavy metals. 3. Growing point and young leaves become yellow or in extreme cases, white. Usually not accompanied by necrosis. 4. Veins and leaflet ends remain green. |
1. These boron-deficient leaves show light general chlorosis.
2. Boron deficiency results in necrosis of meristematic tissues in the growing region, leading to loss of apical dominance and the development of a rosette condition. 3. The leaves are unusually brittle and tend to break easily. |
1. The leaves show light interveinal chlorosis developed under a limited supply of Mn.
2. The early stages of the chlorosis induced by manganese deficiency are somewhat similar to iron deficiency. 3. Browsing spotting occurs on leaflets, especially along larger veins and mid-ribs. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Eggs are minute, oval and yellowish in colour. | Small, pink yellowish with a brown head. | Pupation takes place in rough silken cocoons. Adults are small moths with a silvery body. | Small, narrow-winged & greyish brown, 15 mm wings span. It is nocturnal in habit. |
| Life Cycle: | 3-6 Days. | 5-16 Days. | 7-8 Days. | 15-20 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | In Field: Spray with 0.05% quinalphos or 0.1% carbaryl at 60 days after planting.
In Storage: Fumigate the tubers with CS2 @ 1 kg/27 cu.m. for 48 hrs at 70″F. or methyl bromide @ 1 kg/27 cu.m. for 3 hrs before storage. CS2 is reported to induce sprouting in storage. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Caterpillar | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Eggs are globular in shape, ribbed and whitish in colour. | 4-5 cm long, dirty black in colour and have habit of coiling at slightest touch. | Dark brown in colour. | Medium sized stout with greyish brown wavy lines & spots on fore wings. The moths are active at dusk and are attracted by light. |
| Life Cycle: | 6 Days. | 5 Days. | 7 Days. | 20-25 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | 1% carbaryl poison bait @ 25-60 kg/ha controls the pest effectively. (1kg carbaryl 50WP +10Kg wheat bran + 1kg jaggery & sufficient water). Apply lindane dust @ 125 kg/ha, before planting of potato crop. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Nymphs | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Small, Light green in color. | Yellowish in colour. | Very minute, slender, yellowish and microscopic. | Small, slender, yellowish to brown with fringed wings and drift away on disturbance. |
| Life Cycle: | 1-4 Days. | 1-6 Days. | 4-6 Days. | 30-45 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spraying the crop with 0.02 % phosphamidon or 0.025 % methyl demeton or 0.03 % dimethoate at 10 days interval as per needed. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Microfeed L 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Eggs are deposited in gelatinous masses and survive in the soil or in plant residues. The female produces an average of 500 eggs. | |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Application of carbofuran 3G @ 1kga.i./ha. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Microfeed P 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: | 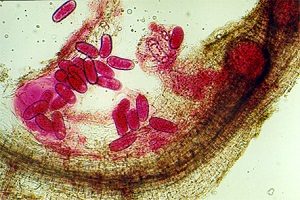 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Substance secreted by the roots of host plants. The larvae then invade the tips of the root and establish a feeding site. Both susceptible and resistant potato varieties will suffer from growth retardation at low and medium populations densities. | |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Use of non fumigant carbofuran 3G @1-2 kg a.i/ha. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Microfeed P 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Seed Variety | Characteristics | Crop Duration (Days) |
Crop Yield (t/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kufri Sindhuri | 1. Medium, round red deep eyes. 2. Moderately resistant to early blight and tolerant to Potato Leaf Roll Virus (PLRV). 3. The slow rate of degeneration. Can tolerate temperature and water stress to some extent. 4. Tolerant to late blight disease. |
110-120 | 40 |
| Kufri Chandramukhi | Large, oval, white, slightly flattened, fleet eyes and dull white flesh. | 80-90 | 25 |
| Kufri Jyoti | 1. Large, oval, white, fleet eyes and white flesh. 2. Moderately resistant to early and late blight. 3. The slow rate of degeneration. |
90-100 | 20 |
| Kufri Lauvkar | 1. Large, round, white, fleet eyes and white flesh. 2. Able to build up yields rapidly under a warmer climate. |
75-80 | 30 |
| Kufri Badshah | 1. Large, oval, white, fleet eyes, dull white flesh, and tubers turn purple on exposure to light. 2. Moderately resistant to early and late blight and resistant to Potato Virus X (PVX). |
100-110 | 50 |
| Kufri Bahar | 1. Large, round-oval, white, medium deep eyes. 2. The slow rate of degeneration. |
100-110 | 45 |
| Kufri Lalima | Large to medium, red, round, medium deep eyes and white flesh. | 100-110 | 40 |
| Kufri Jawahar | Medium, round-oval, creamy white, fleet eyes and pale yellow flesh. | 80-90 | 40 |
| Kufri Sutlej | Large, oval, white, fleet eyes and white flesh. | 90-100 | 40 |
| Kufri Ashoka | 1. Large, oval-long, white, fleet eyes and white flesh. 2. Susceptible to late light. |
70-80 | 40 |
| Kufri Pukhraj | Large, oval, slightly tapered, white, fleet eyes and yellow flesh. | 70-90 | 40 |
| Kufri Chipsona-1 | Medium to large, oval, white, fleet eyes and dull white flesh. | 90-110 | 40 |
| Kufri Chipsona-2 | Medium, Round-oval, white, fleet eyes and yellow flesh. | 90- 110 | 35 |
| Kufri Anand | 1. Medium oval-long, white, flattened, fleet eyes, smooth skin and white flesh. 2. Resistant to late blight and tolerant to frost. |
100-110 | 35-40 |

