- Home
- Crop Knowledge
- Fruits
- Grapes
Grapes
- Nutrients
- Common Pests
- Crop Selection
- Documents
| Duration | 1 Year | 2 Year | 3 Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Nutrients (Kg/vine) |
FYM | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| N | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.60 | |
| P | 0.8 | 0.16 | 0.24 | |
| K | 0.40 | 0.80 | 1.20 | |
Deficiency of Nutrients:
| Nutrients | Nitrogen (N) | Phosphorus (P) | Potassium (K) | Calcium (Ca) | Magnesium (Mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients Deficiency |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Deficiency Symptoms | 1. An overall reduction in growth.
2. Leaves become uniformly light-green or yellow. 3. Reddening of a petiole. 4. Berries may be small. |
1. A dull, dark green colour will appear on the leaves.
2. In mid-to-late summer, leaves may have a bronze colour, especially on the west-facing side of the trellis. 3. Some leaves may have dark spots or blotches. 4. Symptoms of potassium deficiency generally develop in mid-shoot leaves followed by older basal leaves. |
1. Symptoms include brown dead spots or areas throughout the leaf.
2. In severe cases, more than half of the leaves on a vine may show these symptoms. |
1. The growth of the plant is reduced. symptoms are first seen at the growing points of the plant, which may become necrotic and die.
2. Flower buds will fail to develop. 3. The youngest leaves will remain small and deformed and will tend to curl upward at the margins. |
1. Green leaf margins with yellow between the veins.
2. Deficiency of magnesium appears first on basal leaves of shoots as a yellowing between veins. 3. Symptoms progress to dead blotches on the leaves, which may be a rusty-red. |
| Nutrients | Sulphur (S) | Boron (B) | Iron (Fe) | Manganese (Mn) | Zinc (Zn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients Deficiency |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Deficiency Symptoms |
1. Whole orchard or spot-wise stunted growth of pale-green plants. |
1. Poor fruit set clusters will tend to be small, and berries will not fully develop on the rachis.
2. Terminal buds may not break in the spring, and ends of shoots sometimes are distorted. |
1. Leaf veins remain green interveinal portion turns yellow young leaves small but not deformed. | 1. Symptoms first appear as interveinal chlorosis or yellowing of the younger terminal leaves.
|
1. Poor fruit set and stunted shots with small, misshapen leaves foliar application of zinc is the most effective method for treating Zn deficiency. |
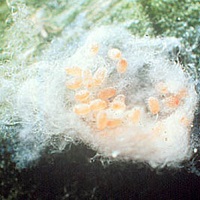
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Yellow to orange, cylindrical in shape, rounded Eggs. | Newly hatched larvae is dark brown in and whole body is cover with back shiny and rectangular. | Pupae bright yellow reddish brown eyes. Wings and legs are off white colour. | Adults are oval in shape, metallic shining blue. |
| Life Cycle: | 10-12 Days. | 25-94 Days. | 7-8 Days. | 10-14 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray with 0.05% malathion or 0.02% phosphamidon or 0.03% dimethoate. First spraying immediately after pruning and second spraying 10 days after sprouting. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Pupae | Nymphs | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | In leaf tissues. | Pupation in soil. | Blackish and Brown in color. | Longevity. |
| Life Cycle: | 3-8 Days. | 2-5 Days. | 11-22 Days. | 18-20 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray with 0.03% dimethoate or 0.02% phosphamidon or thiamethoxam 25 WG 3 gms or spinosad 45 SP 3 ml or fipronil 5% SC 15 ml in 10 lits of water at 15 days interval, first spray immediately after pruning in April and October.
Spray with cytraniprol @ 10.26 OD, Emmamectin Benzoate @ 5.00 SG, Lambda cyhalothrin 4.9 CS, Fipronil 80 WG,, first spray immediately after pruning in April and October. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Microfeed L 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: | 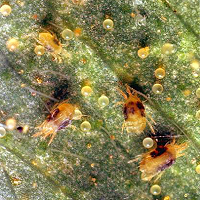 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Egg is 0.7 mm long, and off-white. | The fully-grown larva is white with a brown head. | The pupa is light- colored but becomes darker just prior to emergence. | The shiny-black adults are small. |
| Life Cycle: | 10 Days for the egg to hatch. | 8-12 Days. | 12-14 Days. | 6/10 Weeks. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray the vines with immidacloprid 17.8 SL, Lambda cyhalothrin 4.9 CS, Cytraniprol 10.26 OD. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
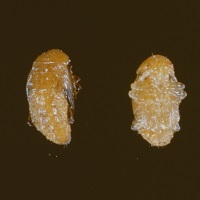
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Nymphs | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | These eggs are orange in color or yellowish white. | The first instars nymphs are also called as crawlers, which are mobile. | The adult female mealybugs are pinkish (M. hirsutus) or yellowish white. |
| Life Cycle: | 5 Days. | Male : 19 Days.
Female : 21 Days. |
30 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spraying of fruit bunches with 0.2% dichlorovos in combination with fish oil rosin soap @ 2.5g/lit or sandovit 1-2 ml / lit (Wetting and sticking agent).
Release of exotic predator Cryptolaemus montrouzieri Mu @ 2500 – 3750/ha. 2-3 spraying with verticellium lecani (Bugicide) 5gm +5 ml milk/10 lits of water at 10-12 days interval wfhen the temperature is less than 30 0C & relative humidity is more than 65% is found effective in controlling the mealy bugs effectively. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Microfeed L 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Nymphs | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Eggs are found on the upper surface of the leaves when the population levels are high. Eggs are also laid in its webbing. | Newly hatched nymphs have translucent larva has six legs. Dark spots appear soon after feeding on the dorsal side. | spots become more distinct. Usually two large, diffuse spots appear forward. Adult spider mite females are reddish. |
| Life Cycle: | 4-6 Days. | 6-8 Days. | 10-14 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Dicofol 18.5 EC @2.50 ml/lit. of water.
OR Fenpyroximate 5 SC @ 1 ml/lit. of water. OR Sulphur 80 WP @ 2 gm/lit. of water. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray Hirsutella or G Agro Verti 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Laid in groups of two to ten on vine. | Small, pale green or pink with median red line. | Blackish, Brown in color. | Small moth. |
| Life Cycle: | 2/4 Days. | 8-18 Days. | 3- 5 Days. | 3-4 Days. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spot application of bubrofezin and acetemprid for effective manage this pest. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit + G Agro Meta 5ml/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Images Of Pest Life Cycle: |  |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages: | Egg | Larvae | Pupae | Adult |
| Mark Of Identification: | Capsule shaped eggs are laid singly in each of the slits and the slits are covered with a hard gummy substance. | Newly hatched flat-headed cream coloured grubs burrow into the trunk or arms and feed inside and make them hollow. | Dark brown in colour. | An adult beetle is about 4 cm long and dull yellow with minute spots. |
| Life Cycle: | 4-5 Days. | 10-15 Days. | 3-5 Days. | 6-8 Weeks. |
Management (Pest Control):
| Chemical: | Spray the vines with 1.5 liters monocrotophos 40 EC or Carbaryl 50 WP. |
|---|---|
| Organic: | Spray G Agro Beau 5gm/lit 2 to 3 spray at 21 days interval. |
| Seed Variety | Characteristics | Crop Yield (t/ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Anab-e-Shahi | 1. This variety is late maturing and heavy yielding. 2. Berries are elongated, medium-large, seeded and amber coloured when fully ripe. 3. Juice is clear and sweet with TSS 14-16%. 4. It is highly susceptible to downy mildew. |
35 |
| Bhokri | 1. Berries are greenish yellow, medium-large, seeded with medium thick skin. 2. Juice is clear with 16-18% TSS. 3. It is susceptible to rust and downy mildew. |
35 |
| Gulabi | 1. Berries are small in size, deep purple, spherical and seeded. 2. TSS is 18-20%. 3. Variety is not susceptible to cracking but it is susceptible to rust and downy mildew. |
10-12 |
| Kali Sahebi | 1. Berries are large, oval cylindrical, reddish-purple and seeded. 2. Variety is susceptible to rust and downy mildew. |
12-18 |
| Perlette | 1. Berries are seedless, small sized, spherical to slightly ellipsoidal and yellowish-green in colour. 2. Variety is not suitable for raisins due to the compactness of clusters. |
35 |
| Thompson Seedless | It has wide adaptability with seedless, ellipsoidal-elongated, golden-yellow berries with medium-thin skin. | 20-25 |
| Arka Neel Mani | 1. Berries are black seedless with crispy pulp having 20-22% TSS. 2. The variety is tolerant to anthracnose. |
28 |
| Arka Shweta | 1. Berries are yellow, ovoid, seedless with 18-19% TSS. 2. Variety is used for table purpose and has good export potential. |
31 |
| Arka Majestic | 1. Berries are deep tan coloured, uniform, round, seeded with 18-20% TSS. 2. Variety is tolerant of anthracnose. |
38 |
| Arka Chitra | 1. Berries are golden yellow with pink blush, slightly elongated having 20-21% TSS. 2. Variety is tolerant to powdery mildew. |
38 |
| Arka Krishna | 1. Berries are dark coloured, seedless, round to ovoid with 20-21% TSS. 2. The variety is suitable for juice making. |
33 |
| Arka Soma | 1. Berries are greenish yellow, round to ovoid. 2. The pulp is meaty and has ‘Muscat’ flavour with 20-21% TSS. 3. The variety is tolerant to anthracnose, downy mildew and powdery mildew. 4. It is good for preparing white dessert wine. |
40 |
| Arka Trishna | 1. Berries are deep tan in colour, round to ovoid with 22-23% TSS. 2. Variety is resistant to anthracnose and tolerant to downy mildew. |
26 |

